
What is a laser?
Laser is a device that can emit laser light. 1954 made the first microwave quantum amplifier, obtained a highly coherent microwave beam. 1958 A.L. Shollo and C.H. Towns microwave quantum amplifier principle to extend the application to the optical frequency range, 1960 T.H. Meyman and others made the first ruby laser. 1961 A. Javan and others made the helium-neon lasers. In 1962, R. N. Hall and others created a gallium arsenide semiconductor laser. Later, the types of lasers are more and more. According to the working medium, lasers can be divided into gas lasers, solid-state lasers, semiconductor lasers and dye lasers 4 categories. Recently, free electron lasers have also been developed, and high-power lasers are usually pulsed output.
What do you know about lasers?
Lasers are one of the essential core components of modern laser processing systems. With the development of laser processing technology, lasers are also moving forward and many new types of lasers have emerged. Early lasers for laser processing were mainly high-power CO2 gas lasers and lamp-pumped solid-state YAG lasers.
At the beginning of the 21st century, another new type of laser, the semiconductor laser, appeared. Compared with traditional lasers, semiconductor lasers have very obvious technical advantages. With the continuous development of semiconductor laser technology, the development of other solid-state lasers based on semiconductor lasers, such as fiber lasers, semiconductor-pumped solid-state lasers, sheet lasers, etc., is also very rapid. Among them, fiber lasers are developing faster, especially rare earth doped fiber lasers.
Those new lasers you probably didn't know about
 Polarized phonon lasers: expected to replace conventional semiconductor lasers.
Polarized phonon lasers: expected to replace conventional semiconductor lasers.
 Polarized Lasers: Light Amplifiers for Stimulated Scattering Polarization (LASSP)
Polarized Lasers: Light Amplifiers for Stimulated Scattering Polarization (LASSP)
 Surface Fiber Lasers: emit laser light radially along the surface of an optical fiber
Surface Fiber Lasers: emit laser light radially along the surface of an optical fiber
 Free-Electron Lasers: High-power coherent radiation sources that are different from conventional lasers.
Free-Electron Lasers: High-power coherent radiation sources that are different from conventional lasers.
 Digital Lasers: The world's first digital lasers were created in Africa.
Digital Lasers: The world's first digital lasers were created in Africa.
 Tapered Refractive Lasers: Tapered refractive lasers are highly efficient and reduce heat treatment.
Tapered Refractive Lasers: Tapered refractive lasers are highly efficient and reduce heat treatment.
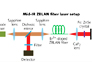 ZBLAN Fiber Laser: First single-frequency ZBLAN fiber laser
ZBLAN Fiber Laser: First single-frequency ZBLAN fiber laser
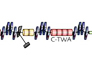 X-ray laser: Smaller device compared to other free-electron lasers
X-ray laser: Smaller device compared to other free-electron lasers
 Room-temperature nano-laser: the smallest room-temperature nano-laser to date
Room-temperature nano-laser: the smallest room-temperature nano-laser to date
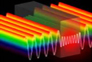 "Superradiant" lasers: based on a powerful engineering technique called "phased arrays".
"Superradiant" lasers: based on a powerful engineering technique called "phased arrays".
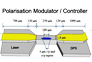 Polarization-controlled lasers: volume manufacturing of semiconductor lasers and related devices
Polarization-controlled lasers: volume manufacturing of semiconductor lasers and related devices
 Quantum cascade lasers: another breakthrough in quantum cascade laser (QCL) technology
Quantum cascade lasers: another breakthrough in quantum cascade laser (QCL) technology
Source: OFweek Laser

Tel. wechat: +86 17665360831(Mr Wu)
Whatsapp: +86 15820436325(Mr. Wu)
Tel. wechat Facebook: +86 13924619027(Windy)
Add: 510 Kunhong building, No. 38 Xinhe Avenue, Xinqiao Street, Baoan District, Shenzhen City, China